Understanding ALS and Dietary Challenges
What is ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)?
ALS is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, gradually leading to muscle weakness, difficulty speaking, swallowing, and breathing. Because of these symptoms, nutrition becomes a major part of managing ALS — and that’s where carefully designed recipes for ALS patients play a crucial role. These recipes are tailored to ensure proper nutrition, while being easy to swallow, digest, and enjoy, even as the disease progresses.
Why Diet Matters in ALS
Proper nutrition helps maintain muscle strength, energy, and overall quality of life. For ALS patients, it’s not just about eating — it’s about eating smart. As swallowing becomes more difficult, meals need to be adapted.
Common Eating Difficulties in ALS Patients
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing (dysphagia)
- Risk of choking
- Fatigue while eating
- Reduced appetite
Key Nutritional Needs for ALS Patients
High-Calorie Requirements
Because of increased energy use from muscle wasting and respiratory effort, ALS patients often require more calories than the average person.
Protein to Prevent Muscle Wasting
Protein is crucial for maintaining what muscle mass remains. Think lean meats, legumes, dairy, and protein powders in meals.
Importance of Hydration
Dry mouth and difficulty swallowing can lead to dehydration. Soups, smoothies, and hydrating foods like fruits can help.
Vitamins and Minerals Support
Key nutrients like Vitamin D, calcium, and B-complex vitamins support nerve health and immunity.
Meal Preparation Tips
Texture Modification
ALS patients often need softer, pureed, or mashed foods to prevent choking. Thickened liquids are also easier and safer to swallow.
Avoiding Choking Hazards
Skip dry, crumbly, or tough foods. Use broths and sauces to moisten meals and blend when needed.
Kitchen Tools to Make Cooking Easier
- High-speed blender
- Food processor
- Ice cream scoop (for portioning soft foods)
- Feeding cups with spouts
Breakfast Recipes
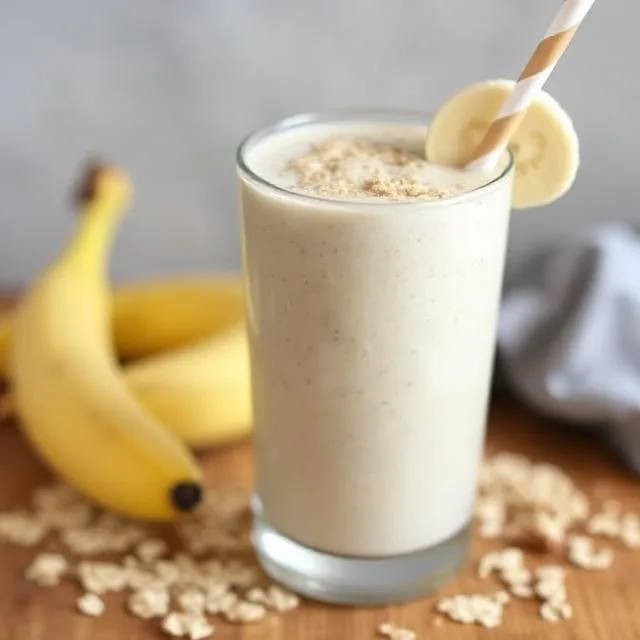

Creamy Banana-Oatmeal Smoothie
Ingredients:
- 1 ripe banana
- ½ cup oats (cooked)
- 1 cup whole milk or almond milk
- 1 tbsp peanut butter
- ½ tsp cinnamon
Instructions:
Blend all ingredients until smooth. Serve warm or chilled.
Scrambled Eggs with Cottage Cheese
Fluffy scrambled eggs mixed with 2 tablespoons of cottage cheese for extra protein and a creamy texture.
Nut Butter & Avocado Toast (Mashed)
Toast soft bread and spread with mashed avocado and almond or peanut butter. Cut into small bites or blend into a savory paste.
Lunch Recipes
Protein-Packed Lentil Soup (Pureed)
Cook red lentils with onions, carrots, and a dash of turmeric. Blend to a smooth consistency and drizzle with olive oil.
Creamy Chicken and Vegetable Mash
Shredded chicken mixed with mashed potatoes, carrots, and peas. Add cream or broth for a smoother texture.
Tuna Salad with Mashed Sweet Potatoes
Mash sweet potatoes and mix with canned tuna and mayonnaise. Serve warm or cold.
Dinner Recipes
Salmon and Spinach Mousse
Ingredients:
- Cooked salmon fillet
- ½ cup steamed spinach
- ¼ cup cream cheese
- Salt & pepper
Blend all until mousse-like. Serve with mashed potatoes or by itself.
Macaroni and Cheese with Hidden Veggies
Use soft pasta and add blended carrots or cauliflower into the cheese sauce for extra nutrition.
Soft Turkey Meatballs in Gravy
Ground turkey meatballs are baked until soft, simmered in thick gravy. Can be mashed for easier swallowing.
Snack & Smoothie Ideas
Greek Yogurt with Honey & Mashed Berries
Use full-fat yogurt, drizzle with honey, and swirl in mashed blueberries or raspberries.
Peanut Butter Banana Shake
Blend milk, banana, peanut butter, and a scoop of vanilla protein for a tasty energy-boosting drink.
Homemade Pudding with Protein Powder
Prepare a soft vanilla or chocolate pudding and add one scoop of unflavored protein powder.
Tips for Caregivers
Meal Planning Ahead
Batch cooking and freezing pureed meals help reduce daily stress. Use labeled containers with reheating instructions.
Making Mealtimes Comfortable
Let meals be unhurried. Use pillows for support and avoid talking while swallowing.
Monitoring Weight & Intake
Track weight weekly and watch for signs of malnutrition. Consult a nutritionist as needed.
Conclusion
Nutrition is a powerful tool in the fight against ALS. While the disease may limit mobility and muscle strength, it should never rob someone of the pleasure of eating. With the right recipes, tools, and support, meals can still be nourishing and enjoyable. Whether you’re preparing food for yourself or a loved one, these recipes offer safety, nutrition, and — most importantly — love in every bite.
FAQs
1. What foods should ALS patients avoid?
Dry crackers, tough meats, nuts, and foods that are hard to chew or swallow should be avoided to reduce the risk.
2. Are supplements necessary for ALS?
In many cases, yes — especially protein powders, vitamins, or high-calorie shakes. Always consult a doctor or nutritionist.
3. Can ALS patients eat solid foods?
Early on, some patients can. Over time, most need softer or pureed options as swallowing becomes more difficult.
4. What is the best smoothie recipe for ALS patients?
A banana, peanut butter, oats, and full-fat milk smoothie provides great calories, protein, and is easy to swallow.
5. How can caregivers help during mealtimes?
Be patient, prepare soft foods, use adaptive utensils, and make mealtime a calm, unhurried experience.
You’ll love also :
phat si-io recipe | ผัดซีอิ๊ว
8 Must-Try Dinner Recipes from Taiwan for Authentic Flavor